The psycopg2 library is a popular PostgreSQL database adapter for Python. While working with databases, it's common to encounter various types of errors. One such error is psycopg2.errors.InvalidDatetimeFormat. This article will delve into what causes the psycopg2.errors.InvalidDatetimeFormat error and provide practical solutions with correct code examples.
What is 'psycopg2.errors.InvalidDatetimeFormat' Error?
The psycopg2.errors.InvalidDatetimeFormat error is raised when the datetime value provided in a SQL query does not match the expected format in the PostgreSQL database. This mismatch can occur due to various reasons, such as incorrect string formatting, timezone issues, or improper data types.
Common Causes of 'psycopg2.errors.InvalidDatetimeFormat' Error
Cause 1: Incorrect String Format
One of the most common causes of this error is providing a datetime string in an incorrect format. PostgreSQL expects datetime values in specific formats, and any deviation can lead to an error.
import psycopg2
# Correct datetime format
datetime_value = '2024-22-07 14:30:00' # Invalid month
connection = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres1", user="postgres", password="1234")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Create table if it doesn't exist
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS events (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
event_time TIMESTAMP
)
""")
# Insert data into the table
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO events (event_time) VALUES (%s)", (datetime_value,))
connection.commit()
print("Data inserted successfully")
cursor.close()
connection.close()
Output
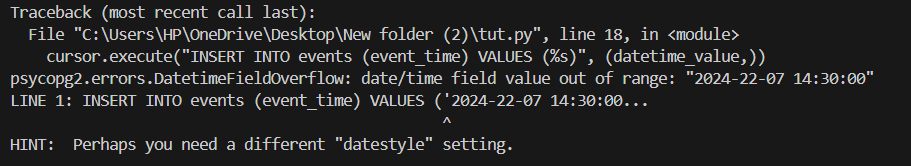
Cause 2: Mismatched Data Types
Another reason for this error is passing a non-datetime data type when the database expects a datetime value. This can happen if the data type conversion is not handled properly in the code.
import psycopg2
# Incorrect data type
datetime_value = 1234567890 # Integer instead of datetime
connection = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres1", user="postgres", password="1234")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Create table if it doesn't exist
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS events (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
event_time TIMESTAMP
)
""")
# Insert data into the table
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO events (event_time) VALUES (%s)", (datetime_value,))
connection.commit()
print("Data inserted successfully")
cursor.close()
connection.close()
Output
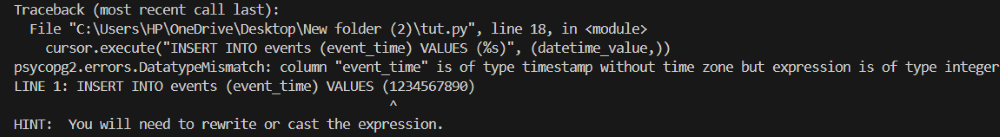
Approaches to Solve 'psycopg2.errors.InvalidDatetimeFormat' Error
Approach 1: Correcting the String Format
Ensure that the datetime string is in the correct format before passing it to the SQL query. PostgreSQL typically expects datetime strings in the format YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS.
import psycopg2
#Correct Information
datetime_value = '2024-07-22 14:30:00'
connection = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres1", user="postgres", password="1234")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Create table if it doesn't exist
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS events (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
event_time TIMESTAMP
)
""")
# Insert data into the table
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO events (event_time) VALUES (%s)", (datetime_value,))
connection.commit()
print("Data inserted successfully")
cursor.close()
connection.close()
Output
Data inserted successfullyApproach 2: Ensuring Correct Data Types
Use Python's datetime module to handle datetime values and ensure that the correct data type is passed to the SQL query.
import psycopg2
#Correct Information
datetime_value = '2024-07-22 14:30:00'
connection = psycopg2.connect(database="postgres1", user="postgres", password="1234")
cursor = connection.cursor()
# Create table if it doesn't exist
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS events (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
event_time TIMESTAMP
)
""")
# Insert data into the table
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO events (event_time) VALUES (%s)", (datetime_value,))
connection.commit()
print("Data inserted successfully")
cursor.close()
connection.close()
Output
Data inserted successfullyConclusion
The psycopg2.errors.InvalidDatetimeFormat error can be a common stumbling block when working with PostgreSQL databases. By understanding its causes—incorrect string formats, mismatched data types, and timezone issues—and applying the appropriate solutions, you can effectively handle this error. Ensuring correct datetime formats and data types, along with proper timezone handling, will help maintain smooth database operations and prevent interruptions in your applications.