Seaborn is a Python library for creating statistical visualizations. It provides clean default styles and color palettes, making plots more attractive and easier to read. Built on top of Matplotlib and integrated with pandas data structures, Seaborn makes data visualization easier and more consistent.
- Seaborn emphasizes visualization as an essential part of data analysis.
- Its dataset-oriented APIs allow switching between different plot types for the same variables.
- Helps in understanding patterns, trends and relationships within the data.
Different Categories of plot in Seaborn
Plots are basically used for visualizing the relationship between variables. Those variables can be either completely numerical or a category like a group, class, or division. Seaborn divides the plot into the below categories:
- Relational plots: This plot is used to understand the relation between two variables.
- Categorical plots: This plot deals with categorical variables and how they can be visualized.
- Distribution plots: This plot is used for examining univariate and bivariate distributions
- Regression plots: The regression plots in Seaborn are primarily intended to add a visual guide that helps to emphasize patterns in a dataset during exploratory data analyses.
- Matrix plots: A matrix plot is an array of scatterplots.
- Multi-plot grids: It is a useful approach to draw multiple instances of the same plot on different subsets of the dataset.
Installation of Seaborn Library
For Python environment:
pip install seaborn
For conda environment:
conda install seaborn
Dependencies for Seaborn Library
There are some libraries that must be installed before using Seaborn. Here we will list out some basics that are a must for using Seaborn.
- Python 3.6 or higher
- numpy (>= 1.13.3)
- scipy (>= 1.0.1)
- pandas (>= 0.22.0)
- matplotlib (>= 2.1.2)
Note: Most of these dependencies are automatically installed when you install Seaborn, but it is important to have compatible versions to avoid errors.
Some basic plots Using seaborn
Histplot: Seaborn Histplot is used to visualize the univariate set of distributions(single variable). It plots a histogram, with some other variations like kdeplot and rugplot. The Histplot function takes several arguments but the important ones are:
- data: This is the array, series, or dataframe that you want to visualize. It is a required parameter.
- x: This specifies the column in the data to use for the histogram. If your data is a dataframe, you can specify the column by name.
- y: This specifies the column in the data to use for the histogram when you want to create a bivariate histogram. By default, it is set to None, meaning that a univariate histogram will be plotted.
- bins: This specifies the number of bins to use when dividing the data into intervals for plotting. By default, it is set to "auto", which uses an algorithm to determine the optimal number of bins.
- kde: This parameter controls whether to display a kernel density estimate (KDE) of the data in addition to the histogram. By default, it is set to False, meaning that a KDE will not be plotted.
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(style="white")
rs = np.random.RandomState(10)
d = rs.normal(size=100)
sns.histplot(d, kde=True, color="m")
Output
.png)
Distplot: Seaborn distplot is used to visualize the univariate set of distributions(Single features) and plot the histogram with some other variations like kdeplot and rugplot.
The function takes several parameters, but the most important ones are:
- a: This is the array, series, or list of data that you want to visualize. It is a required parameter.
- bins: This specifies the number of bins to use when dividing the data into intervals for plotting. By default, it is set to "auto", which uses an algorithm to determine the optimal number of bins.
- kde: This parameter controls whether to display a kernel density estimate (KDE) of the data in addition to the histogram. By default, it is set to True, meaning that a KDE will be plotted.
- hist: This parameter controls whether to display the histogram of the data. By default, it is set to True, meaning that a histogram will be plotted.
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(style="white")
rs = np.random.RandomState(10)
d = rs.normal(size=100)
colors = ["r", "g", "b"]
sns.distplot(d, kde=True, hist=True, bins=10,
rug=True,hist_kws={"alpha": 0.3,
"color": colors[0]},
kde_kws={"color": colors[1], "lw": 2},
rug_kws={"color": colors[2]})
Output
.png)
Note: The distplot function has been deprecated in the newer version of the Seaborn Library
Lineplot: The line plot is one of the most basic plots in the seaborn library. This plot is mainly used to visualize the data in the form of some time series, i.e. in a continuous manner.
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.set(style="dark")
fmri = sns.load_dataset("fmri")
sns.lineplot(x="timepoint",
y="signal",
hue="region",
style="event",
data=fmri)
plt.show()
Output
.webp)
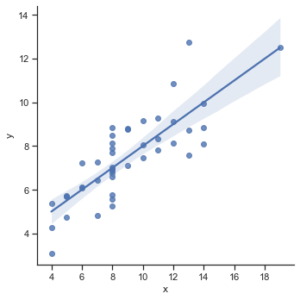
Lmplot: The lmplot is another most basic plot. It shows a line representing a linear regression model along with data points on the 2D space and x and y can be set as the horizontal and vertical labels respectively.
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(style="ticks")
df = sns.load_dataset("anscombe")
sns.lmplot(x="x", y="y", data=df)