In this article, we will see how to query and select specific columns using SQLAlchemy in and
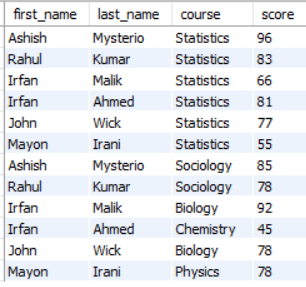
For our examples, we have already created a Students table which we will be using:
Selecting specific column in SQLAlchemy:
Syntax: sqlalchemy.select(*entities)
Where: Entities to SELECT from. This is typically a series of ColumnElement for Core usage and ORM-mapped classes for ORM usage.
SQLAlchemy Core
In this example, we have used the SQLAlchemy Core. The already created students table is referred which contains 4 columns, namely, first_name, last_name, course, and score. But we will be only selecting a specific column. In the example, we have referred to the first_name and last_name columns. Other columns can also be provided in the entities list.
By using the select() method:
import sqlalchemy as db
# Define the Engine (Connection Object)
engine = db.create_engine("mysql+pymysql://\
root:password@localhost/Geeks4Geeks")
# Create the Metadata Object
meta_data = db.MetaData()
meta_data.reflect(bind=engine)
#don't follow the following syntax for creating the meta_data
#meta_data=MetaData(bind=engine)
#Here MetaData class doesn't have any argument bind,so we get arror.
# Get the `students` table from the Metadata object
STUDENTS = meta_data.tables['students']
# SQLAlchemy Query to SELECT specific column
query = db.select(
STUDENTS.c.first_name,
STUDENTS.c.last_name
)
#don't use [STUDENT.c.first_name,....] give ArgumentError
#[STUDENT.c.first_name,....] the syntax in older versions only
# Fetch all the records
result = engine.execute(query).fetchall()
# View the records
for record in result:
print("\n", record[0], record[1])
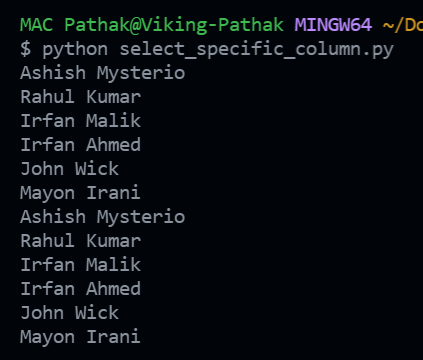
Output:
SQLAlchemy ORM
This example is similar to the previous one except for the fact that it is built on SQLAlchemy ORM. SQLAlchemy ORM is a more pythonic implementation of the SQLAlchemy, as you can see in the code, that we have created a Python class to refer to the student table. The syntax is the same in both cases with a minor change in the way we are defining the column names. The columns in ORM are defined using ORM-mapped classes. The output is the same for both as we have taken the first_name and last_name columns in this example as well.
By using the select method():
import sqlalchemy as db
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
# DEFINE THE ENGINE (CONNECTION OBJECT)
engine = db.create_engine("mysql+pymysql:/\
/root:password@localhost/Geeks4Geeks")
# CREATE THE TABLE MODEL TO USE IT FOR QUERYING
class Students(Base):
__tablename__ = 'students'
first_name = db.Column(db.String(50),
primary_key=True)
last_name = db.Column(db.String(50),
primary_key=True)
course = db.Column(db.String(50))
score = db.Column(db.Float)
# SQLAlCHEMY CORE QUERY TO FETCH SPECIFIC COLUMNS
query = db.select([Students.first_name, Students.last_name])
# FETCH ALL THE RECORDS IN THE RESPONSE
result = engine.execute(query).fetchall()
# VIEW THE ENTRIES IN THE RESULT
for record in result:
print(record[0], record[1])
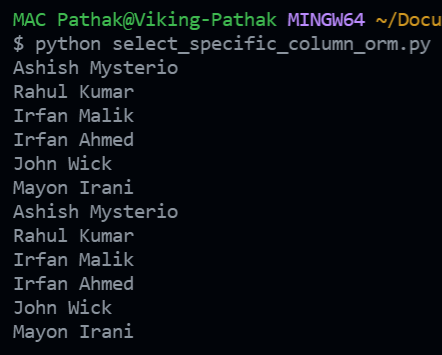
Output:
By using ORM query() method:
We can also use the query() method to select the specific columns or all columns of the table.
query(): The query() method in SQLAlchemy is used to create a query object that allows you to perform database queries using SQLAlchemy's ORM.
Syntax: query(ModelClass or ModelClass.attributes)
retruns the instance of the Query class in SQLAlchemy ORM.
Note: query() method does not work with SQLAlchemy Core, because the query() method is not directly available to the SQLAlchemy Core.
import sqlalchemy as db
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
# DEFINE THE ENGINE (CONNECTION OBJECT)
engine = db.create_engine("mysql+pymysql:/\
/root:password@localhost/Geeks4Geeks")
# CREATE THE TABLE MODEL TO USE IT FOR QUERYING
class Students(Base):
__tablename__ = 'students'
first_name = db.Column(db.String(50),
primary_key=True)
last_name = db.Column(db.String(50),
primary_key=True)
course = db.Column(db.String(50))
score = db.Column(db.Float)
# SQLAlCHEMY ORM qury() TO FETCH SPECIFIC COLUMNS
query = session.query(Students.first_name, Students.last_name)
# executing the query with db
result = query().all()
# VIEW THE ENTRIES IN THE RESULT
for record in result:
print(record[0], record[1])
Output:
Ashish Mysterio
Rahul Kumar
Irfan Malik
Irfan Ahmed
John Wick
Mayon Irani
Ashish Mysterio
Rahul Kumar
Irfan Malik
Irfan Ahmed
John Wick
Mayon Irani
By using text() method:
we can use the text() method to select columns from the table. It worksallows with both SQLAlchemy ORM and SQLAlchemy Core.
text(): it allows us to write SQL queries directly in your code as strings.
Syntax: text('SQL_QUERY')
returns TextClause object which represents a textual SQL expression
#Creating the SQL statementby using the text()
stmt=text("SELECT first_name,last_name FROM students")
#executing the statement with DB
res=session.execute(stmt)
for val in res:
print(val[0],val[1])
Note: we can use update , delete, insert, etc..statements with the text() method.