Authentication is a key part of securing any web application. In Django REST Framework (DRF), Basic Authentication provides a simple way to verify users using their username and password. This method builds upon Django’s built-in authentication system, allowing APIs to restrict access and ensure only authorized users can interact with protected endpoints.
User Authentication System in Django
Step 1: Create the Django project and app
django-admin startproject core
cd core
python manage.py startapp authentication
File Structure:

Step 2: Register app name in Installed_Apps in settings.py file.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
"django.contrib.admin",
"django.contrib.auth",
"django.contrib.contenttypes",
"django.contrib.sessions",
"django.contrib.messages",
"django.contrib.staticfiles",
"authentication", // App name
]
Step 3: views.py
The views handle rendering templates and processing form data for login, registration, and the home page.
- home(request)
Renders the home.html template when users access the home page. - login_page(request)
Handles user login. On a POST request, it retrieves username and password from the form. It checks if the user exists; if not, it displays an error message and redirects back to the login page. - register_page(request)
Handles user registration. On a POST request, it retrieves first_name, last_name, username, and password from the form. It checks if the username is already taken; if so, it displays a message and redirects back to the registration page.
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from django.contrib import messages
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from .models import *
def home(request):
return render(request, 'home.html')
def login_page(request):
if request.method == "POST":
username = request.POST.get('username')
password = request.POST.get('password')
# Check if a user with the provided username exists
if not User.objects.filter(username=username).exists():
# Display an error message if the username does not exist
messages.error(request, 'Invalid Username')
return redirect('/login/')
user = authenticate(username=username, password=password)
if user is None:
# Display an error message if authentication fails (invalid password)
messages.error(request, "Invalid Password")
return redirect('/login/')
else:
login(request, user)
return redirect('/home/')
return render(request, 'login.html')
# Define a view function for the registration page
def register_page(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
first_name = request.POST.get('first_name')
last_name = request.POST.get('last_name')
username = request.POST.get('username')
password = request.POST.get('password')
# Check if a user with the provided username already exists
user = User.objects.filter(username=username)
if user.exists():
# Display an information message if the username is taken
messages.info(request, "Username already taken!")
return redirect('/register/')
# Create a new User object with the provided information
user = User.objects.create_user(
first_name=first_name,
last_name=last_name,
username=username
)
# Set the user's password and save the user object
user.set_password(password)
user.save()
# Display an information message indicating successful account creation
messages.info(request, "Account created Successfully!")
return redirect('/register/')
return render(request, 'register.html')
Step 4: models.py
- Import the models module from Django to create and manage database models.
- Import the User model from django.contrib.auth.models, which provides Django’s built-in authentication system for handling user data and permissions.
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
Migrate models:
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
Create the superuser:
python manage.py createsuperuser
Step 5:urls.py
This file defines URL routes and connects them to views within the Django application.
- Imports required modules for URL routing, views, admin interface, and file handling.
- Defines URL patterns for the home, admin, login, and registration pages.
- Serves media and static files during development.
# Import required modules
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from authentication.views import *
from django.conf import settings
from django.contrib.staticfiles.urls import staticfiles_urlpatterns
from django.conf.urls.static import static
# Define URL patterns
urlpatterns = [
path('home/', home, name="home"), # Home page
path("admin/", admin.site.urls), # Admin interface
path('login/', login_page, name='login_page'), # Login page
path('register/', register_page, name='register'),# Registration page
]
# Serve media files in development mode
if settings.DEBUG:
urlpatterns += static(settings.MEDIA_URL, document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)
# Serve static files
urlpatterns += staticfiles_urlpatterns()
Update settings.py for Media and Static Files:
import os
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATIC_ROOT= os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'staticfiles')
STATICFILES_DIR = {
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'public/static')
}
MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'public/static')
MEDIA_URL = '/media/'
Templates Folder
Step 6.1: login.html
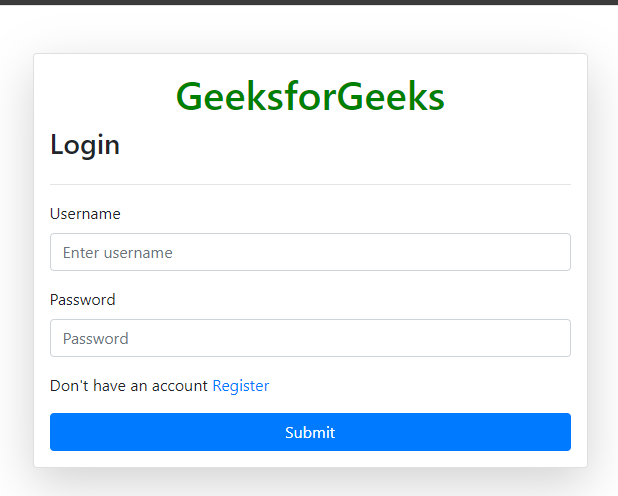
Below template provides a login page for users. It uses Bootstrap 4.5.2 for styling and includes CSRF protection for security.
- The GeeksforGeeks title is centered and highlighted in green.
- CSRF token is included to prevent cross-site request forgery attacks.
- Displays error or success messages using Bootstrap alerts.
- Input fields for username and password, both required.
- Link to the registration page for new users.
- Submit button to log in.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Login</title>
<link href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<!-- Login form -->
<form class="col-6 mx-auto card p-3 shadow-lg" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<h1 style="text-align: center;"><span style="color: green;">GeeksforGeeks</span></h1>
{% csrf_token %} <!-- CSRF token for security -->
<!-- Login heading -->
<h3>Login</h3>
<hr>
<!-- Display error/success messages -->
{% if messages %}
<div class="alert alert-primary" role="alert">
{% for message in messages %}
{{ message }}
{% endfor %}
</div>
{% endif %}
<!-- Username input field -->
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Username</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="username" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp"
placeholder="Enter username" required>
</div>
<!-- Password input field -->
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Password</label>
<input type="password" name="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password" required>
</div>
<!-- Link to registration page -->
<p>Don't have an account <a href="/register/">Register</a> </p>
<!-- Submit button -->
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Step 6.2: register.html
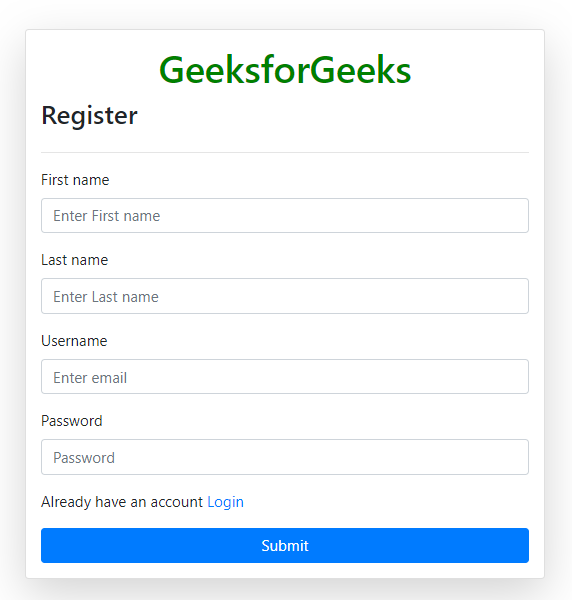
This template provides a registration form for new users. It uses Bootstrap 4.5.2 for styling and includes CSRF protection for security.
- CSRF token is included to prevent cross-site request forgery attacks.
- Displays error or success messages using Bootstrap alerts.
- Input fields for first name, last name, username, and password (all required).
- Link to the login page for users who already have an account.
- Submit button to register a new user.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<title>Registration Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<!-- Registration form -->
<form class="col-6 mx-auto card p-3 shadow-lg" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{% csrf_token %} <!-- CSRF token for security -->
<!-- Registration form heading -->
<h1 style="text-align: center;"><span style="color: green;">GeeksforGeeks</span></h1>
<h3>Register</h3>
<hr>
<!-- Display error/success messages -->
{% if messages %}
<div class="alert alert-primary" role="alert">
{% for message in messages %}
{{ message }}
{% endfor %}
</div>
{% endif %}
<!-- First Name input field -->
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">First name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp"
placeholder="Enter First name" name="first_name" required>
</div>
<!-- Last Name input field -->
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Last name</label>
<input type="text" name="last_name" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1"
aria-describedby="emailHelp" placeholder="Enter Last name" required>
</div>
<!-- Username input field -->
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Username</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="username" id="exampleInputEmail1"
aria-describedby="emailHelp" placeholder="Enter email" required>
</div>
<!-- Password input field -->
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" name="password" id="exampleInputPassword1"
placeholder="Password" required>
</div>
<!-- Link to login page for users who already have an account -->
<p>Already have an account <a href="/login/">Login</a> </p>
<!-- Submit button -->
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Step 6.3: home.html
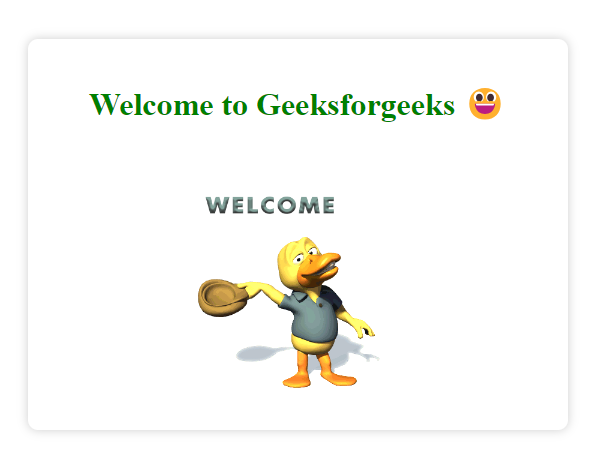
This template displays a welcoming page for users. It includes a heading and an animated GIF for a friendly user experience.
- Page title styled in green using inline CSS.
- .container class centers content and adds a white background with a subtle shadow.
- h1 tag styles the heading in green and bold.
- img tag displays an animated GIF at 60% width.
- The page content is contained within a centered container for a clean layout.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title style="color: green;">Welcome to Geeksforgeeks ????</title>
<style>
.container {
text-align: center;
margin: 100px auto;
max-width: 500px;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}
h1 {
color: green;
font-weight: bold;
}
img {
width: 60%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<!-- Page heading -->
<h1>Welcome to Geeksforgeeks </h1>
<!-- Animated GIF -->
<!-- Use "welcome.gif" as the source for the GIF -->
<img src="https://i.ibb.co/RNB6jpM/welcome.gif" alt="Welcome Cartoon">
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Step 7: Run the Development Server
Start the Django development server to test the authentication system and templates:
- Opens the project on http://127.0.0.1:8000/ or http://localhost:8000/.
- Test the login page at /login/.
- Test the registration page at /register/.
- After login or registration, you will be redirected to the home page displaying the welcome message and GIF.