FloatLayout in Kivy is used to place widgets using relative positions and sizes. Widgets are positioned using percentage-based values so they move and resize automatically when the window size changes.
Example: In this example, a text input box is placed inside a FloatLayout using relative size and position.
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.floatlayout import FloatLayout
from kivy.uix.textinput import TextInput
class Main(FloatLayout):
def __init__(self, **kw):
super().__init__(**kw)
t = TextInput(text="Enter name", size_hint=(.5, .1), pos_hint={'x': .25, 'y': .45})
self.add_widget(t)
class Demo(App):
def build(self):
return Main()
Demo().run()
Output
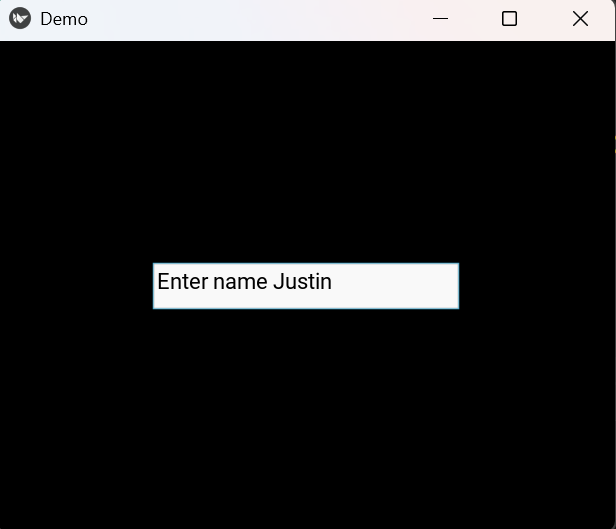
Explanation:
- FloatLayout() creates a layout that uses relative positioning.
- TextInput(text="Enter name") creates a typing box.
- size_hint=(.5, .1) sets the width to 50% and height to 10% of the window.
- pos_hint={'x': .25, 'y': .45} positions the box using percentages.
- add_widget(t) adds the text box to the layout.
Syntax
FloatLayout(size_hint=None, pos_hint=None)
Parameters:
- size_hint: Controls width and height using values from 0 to 1
- pos_hint: Controls widget position using keys like x, y, top, right
Examples
Example 1: In this example, a button is placed using fixed pixel coordinates.
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.floatlayout import FloatLayout
from kivy.uix.button import Button
class Main(FloatLayout):
def __init__(self, **kw):
super().__init__(**kw)
b = Button(text="Click", size_hint=(.3, .2), pos=(200, 150))
self.add_widget(b)
class Demo(App):
def build(self):
return Main()
Demo().run()
Output
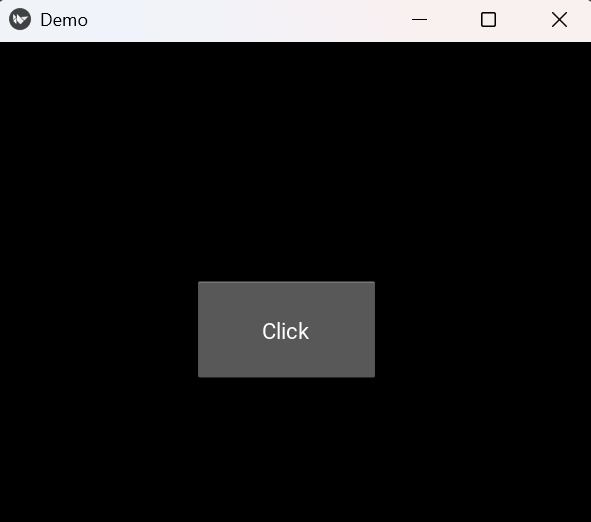
Explanation:
- Button(text="Click") creates a button.
- size_hint=(.3, .2) sets its size relative to the window.
- pos=(200, 150) sets the button’s exact screen position.
- add_widget(b) places the button inside FloatLayout.
Example 2: In this example, two widgets are placed at different positions using relative coordinates.
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.floatlayout import FloatLayout
from kivy.uix.button import Button
from kivy.uix.textinput import TextInput
class Main(FloatLayout):
def __init__(self, **kw):
super().__init__(**kw)
self.add_widget(TextInput(text="Name", size_hint=(.4, .1), pos_hint={'x': .1, 'y': .6}))
self.add_widget(Button(text="OK", size_hint=(.3, .15), pos_hint={'x': .5, 'y': .3}))
class Demo(App):
def build(self):
return Main()
Demo().run()
Output
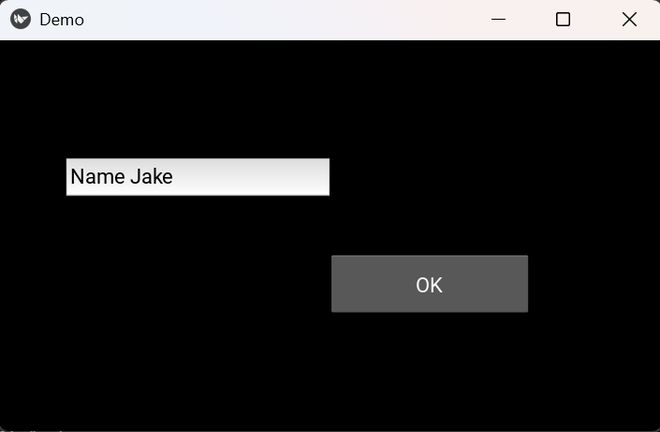
Explanation:
- TextInput(...) creates an input box at a relative location.
- Button(...) places a button at another relative position.
- pos_hint controls where each widget appears.
- FloatLayout keeps both widgets aligned when the window resizes.