Java provides a rich set of built-in packages that contain predefined classes and interfaces to perform common programming tasks. These packages help developers write efficient, reusable, and reliable code without having to build everything from scratch.
import java.lang.String;
import java.lang.Math;
import java.lang.System;
public class GFG{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Java";
int max = Math.max(10, 20);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(max);
}
}
Output
Java 20
Explanation: The program uses classes from the built-in java.lang package to perform basic operations. String stores text, Math.max() finds the maximum value, and System.out.println() prints the output to the console.
Hierarchical Structure of Java Packages
The image below demonstrates the hierarchical structure of Java packages and their related class files.
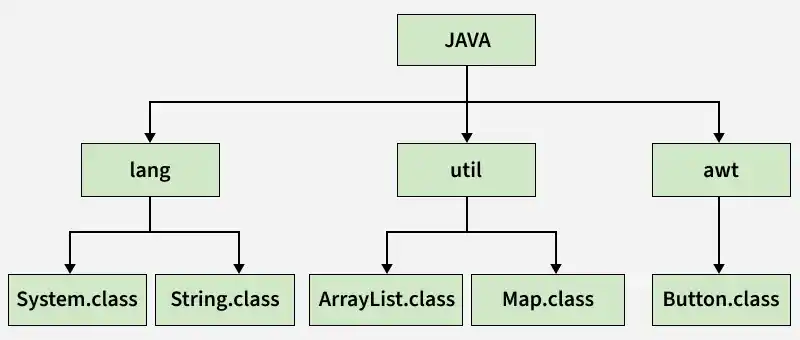
Important Built-in Packages in Java
Below are some of the most commonly used built-in packages provided by Java for handling core programming tasks.
1. java.sql Package
The java.sql package provides APIs for performing database operations using JDBC (Java Database Connectivity).
import java.sql.*;
public class Geeks {
static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/Geeksforgeeks";
static final String USER = "user";
static final String PASSWORD = "123";
static final String QUERY = "SELECT ID, NAME, ADDRESS FROM STUDENTS";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Open a connection
try(
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
Statement stm = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stm.executeQuery(QUERY);) {
while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieving data from column name
System.out.print("ID: " + rs.getInt("id"));
System.out.print(",NAME: " + rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(",ADDRESS: " + rs.getString("address"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output
ID: 1, NAME: Harry, ADDRESS: India
ID: 2, NAME: Jhon, ADDRESS: USA
ID: 3, NAME: Kim, ADDRESS: USA
ID: 4, NAME: Bob, ADDRESS: India
Explanation:
- We can see that first, we imported the package name java.sql.*,
- In the main method, we initialize the string variable name URL, USER, PASSWORD, QUERY.
- And then use DriverManager to get a connection to the database and finally, we use the executeQuery method to execute the query of selecting the data from the database.
2. java.lang Package
The java.lang package contains core classes that are fundamental to the Java language. This package is automatically imported into every Java program, allowing its classes to be used without explicit import statements.
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 100, b = 200;
int maxi = Math.max(a, b);
System.out.printf("Maximum is = %d%n", maxi);
}
}
Output
Maximum is = 200
Explanation:
- We use the lang package and Math class to find the maximum of two-digit using the "max" function.
- First, we created a three integer variable named "a" and "b" and maxi. where a = 100 and b = 200 and maxi will store the maximum value from a or b.
- After assigning values to the variable we used the max function to find the maximum and stored it in maxi.
- So, in desired output, we can see a maximum of two numbers and that is 200.
3. java.util Package
The java.util package provides utility classes such as collections, date and time utilities, and array manipulation tools. One of the most commonly used classes in this package is Arrays, which offers helpful methods for array operations
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 40, 30, 20, 70, 80 };
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println("Sorted Array is = " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
Output:
Sorted Array is = [20, 30, 40, 70, 80]Explanation:
- We used java.util package and Arrays class to sort the integer array.
- First, we created an integer type array that consists of elements 40,30,20,70,80 and sort the array using the "sort" function of the Arrays class.
- After sorting an array it prints the sorted array.
4. java.io Package
The java.io package provides classes and interfaces for handling input and output operations, including reading user input and performing file handling tasks such as reading from or writing to files.
import java.io.Console;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Console cons = System.console();
if (cons != null) {
System.out.println("Enter your favorite color:");
String colour = cons.readLine();
System.out.println("Favorite colour is " + colour);
} else {
System.out.println("Console not available.");
}
}
}
Output
Enter your favorite color
RED
Favorite color is RED
Explanation:
- We use the java.io package and Console class to take input from users to perform some task or operations on it and then finally display the result on the console.
- As code said first we display the message "Enter your favorite color" which asks a user to enter color.
- Then user system read that line using cons.readLine() and stored it in string type variable then finally display that line.
5. Java.net Package
The java.net package contains classes and interfaces for network programming, such as Socket, ServerSocket, DatagramSocket, and URL. Java supports networking using both TCP and UDP protocols.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port_no = 4567;
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(port_no);
byte[] receive = new byte[65535];
DatagramPacket DpReceive;
while (true) {
DpReceive = new DatagramPacket(receive, receive.length);
ds.receive(DpReceive);
System.out.println("DATA:- " + data(receive));
receive = new byte[65535];
}
}
public static String data(byte[] a) {
if (a == null) return null;
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
int i = 0;
while (a[i] != 0) {
ret.append((char) a[i]);
i++;
}
return ret.toString();
}
}
Output:
DATA:- //whatever to get from server Explanation:
- Here we have implemented a UDP socket receiver that receives data from the server-side through port no.
- First, we created a socket using the DatagramSocket method to listen on port no 4567, second, we created a datagram packet to receive the data in byte buffer and then finally after getting the data we printed it.
6. Java.awt Package
The java.awt package provides classes for building graphical user interfaces and handling graphics in Java. It includes basic GUI components, many of which are extended by the javax.swing package.
import java.awt.*;
public class Geeks {
AWTExample() {
Frame fr1 = new Frame();
Label la = new Label("Welcome to Java Graphics - GEEKSFORGEEKS");
fr1.add(la);
fr1.setSize(300, 200);
fr1.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new AWTExample();
}
}
Output:

Explanation: Here, we created a frame of size 200 x 200 by using an awt package and then print a message "Welcome to the Java graphics GEEKSFORGEEKS.
