The Collections class in Java is a utility class provided by the Java Collections Framework that contains static methods for performing common operations on collections. It simplifies tasks like sorting, searching, and modifying collection elements efficiently.
- Provides methods such as sort(), reverse(), shuffle(), and binarySearch()
- Helps improve code readability and performance without manual implementation
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Geeks {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an ArrayList to store elements
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>();
// Add elements to the list
al.add("Apple");
al.add("Banana");
al.add("Apple"); // Duplicates are allowed
System.out.println("" + al);
}
}
Output
[Apple, Banana, Apple]
Explanation: An ArrayList of type String is created and elements are added to it, including a duplicate value. The output shows that ArrayList maintains insertion order and allows duplicate elements.
Collection Class Declaration
public class Collections extends Object
Object is the parent class of all the classes.
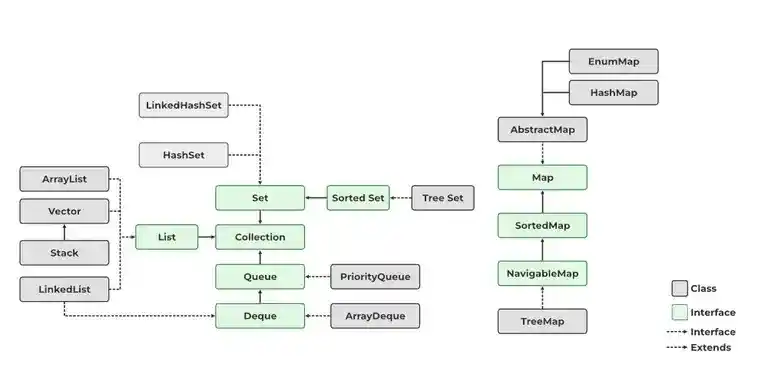
Java Collections Classes
Collection Framework contains both classes and interfaces. Although both seem the same but there are certain differences between Collection classes and the Collections framework.
To know more about ->Collection vs Collections
The Collection classes in Java are mentioned below:
1. List Implemented Classes
Lists are ordered collections that allow duplicates.
- ArrayList: A resizable array that maintains insertion order. Allows duplicates and provides fast random access.
- LinkedList: Implements a doubly-linked list. Can be used as List, Stack, or Queue.
- Vector: Synchronized resizable array. Slower than ArrayList but thread-safe.
- Stack: Extends Vector. Follows LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) principle for storing elements.
2. Set Implemented Classes
Sets are unordered collections that do not allow duplicates.
- HashSet: Stores elements in a hash table. Offers fast insertion, deletion, and search.
- LinkedHashSet: Maintains insertion order using a doubly-linked list internally.
- TreeSet: Stores elements in sorted order. Implements SortedSet and ensures natural or custom ordering.
3. Queue Implemented Classes
Queues hold elements prior to processing, typically following FIFO, but can support priority.
- PriorityQueue: Orders elements based on priority or a custom comparator.
- ArrayDeque: Double-ended queue using a resizable array. Can function as a stack or queue.
- LinkedList: Can also be used as a Queue. Maintains insertion order and allows duplicates
4. Map Implemented Classes
Maps store key-value pairs with unique keys. Not part of the Collection interface but part of JCF.
- HashMap: Stores key-value pairs with fast access. Allows one null key and multiple null values.
- LinkedHashMap: Maintains insertion order of keys.
- TreeMap: Keys are sorted either naturally or with a custom comparator.
- Hashtable: Synchronized map. Does not allow null keys or null values.
- EnumMap: Specialized map for enum keys. Efficient storage and fast access.
- WeakHashMap: Uses weak references for keys. Unreferenced keys can be garbage collected.
- IdentityHashMap: Uses reference equality (==) instead of equals() for key comparison.
- ConcurrentHashMap: Thread-safe map optimized for concurrent access by multiple threads.
5. Abstract Base Classes
These classes provide common functionalities and simplify implementation of concrete collection classes.
- AbstractCollection: Base class for implementing custom collections.
- AbstractList: Base class for List implementations. Provides default methods for lists.
- AbstractSet: Base class for Set implementations. Provides default methods for sets.
- AbstractMap: Base class for Map implementations. Simplifies map creation.
- AbstractQueue: Base class for Queue implementations. Provides basic queue operations.
Examples of Collections Operations
1. Adding Elements
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class AddExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
Collections.addAll(list, "Mango", "Grapes");
System.out.println("After Adding: " + list);
}
}
Output
After Adding: [Apple, Banana, Mango, Grapes]
Explanation
- Creates an ArrayList to store String elements dynamically.
- Adds elements using add() and multiple elements at once using Collections.addAll().
- Maintains insertion order and allows duplicates.
2. Deleting Elements
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Mango");
list.add("Grapes");
// Remove element by value
list.remove("Banana");
// Remove element by index
list.remove(0);
// Print final list
System.out.println("After Removing: " + list);
}
}
Output
After Removing: [Mango, Grapes]
Explanation
- Creates an ArrayList to store string elements dynamically.
- remove("Banana") deletes an element by value, while remove(0) deletes by index.
- Elements automatically shift after removal.
- Prints the updated list.
3. Searching Elements
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Mango");
// Searching for an element
if (list.contains("Mango")) {
System.out.println("Mango is present in the list");
}
}
}
Output
Mango is present in the list
Explanation
- Creates an ArrayList to store String elements.
- Adds elements using the add() method.
- contains("Mango") checks whether "Mango" exists in the list.
- Prints a message if the element is found.
4. Updating Elements
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class UpdateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Mango");
// Updating element at index 0
list.set(0, "Orange");
// Print updated list
System.out.println("After Updating: " + list);
}
}
Output
After Updating: [Orange, Banana, Mango]
Explanation
- Creates an ArrayList to store String elements.
- Adds elements using add() method.
- set(0, "Orange") replaces the element at index 0.
5. Sorting a Collection
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class SortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> fruits = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements
fruits.add("Banana");
fruits.add("Apple");
fruits.add("Mango");
fruits.add("Grapes");
// Sorting the list in ascending order
Collections.sort(fruits);
// Print sorted list
System.out.println("After Sorting: " + fruits);
}
}
Output
After Sorting: [Apple, Banana, Grapes, Mango]
Explanation:
- Creates an ArrayList named fruits.
- Adds multiple fruit names to the list.
- Collections.sort(fruits) sorts elements in ascending (natural) order.
Methods of Collections Class
Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T... elements) | This method is used to insert the specified collection elements to the specified collection. |
| asLifoQueue(Deque<T> deque) | This method returns a view of a Deque as a Last-in-first-out (Lifo) Queue. |
| binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable> list, T key) | This method searches the key using binary search in the specified list. |
| binarySearch(List<? extends T> list, T key, Comparator<? super T> c) | This method searches the specified list for the specified object using the binary search algorithm. |
| checkedCollection(Collection<E> c, Class<E> type) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified collection. |
| checkedList(List<E> list, Class<E> type) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified list. |
| checkedMap(Map<K,V> m, Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified map. |
| checkedNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K,V> m, Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified navigable map. |
| checkedNavigableSet(NavigableSet<E> s, Class<E> type) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified navigable set. |
| checkedQueue(Queue<E> queue, Class<E> type) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified queue. |
| checkedSet(Set<E> s, Class<E> type) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified set. |
| checkedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m, Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified sorted map. |
| checkedSortedSet(SortedSet<E> s, Class<E> type) | This method returns a dynamically typesafe view of the specified sorted set. |
| copy(List<? super T> dest, List<? extends T> src) | This method copies all of the elements from one list into another. |
| disjoint(Collection<?> c1, Collection<?> c2) | This method returns true if the two specified collections have no elements in common. |
| emptyEnumeration() | This method returns an enumeration that has no elements. |
| emptyIterator() | This method returns an iterator that has no elements. |
| emptyList() | This method returns an empty list (immutable). |
| emptyListIterator() | This method returns a list iterator that has no elements. |
| emptyMap() | This method returns an empty map (immutable). |
| emptyNavigableMap() | This method returns an empty navigable map (immutable). |
| emptyNavigableSet() | This method returns an empty navigable set (immutable). |
| emptySet() | This method returns an empty set (immutable). |
| emptySortedMap() | This method returns an empty sorted map (immutable). |
| emptySortedSet() | This method returns an empty sorted set (immutable). |
| enumeration(Collection<T> c) | This method returns an enumeration over the specified collection. |
| fill(List<? super T> list, T obj) | This method replaces all of the elements of the specified list with the specified element. |
| frequency(Collection<?> c, Object o) | This method returns the number of elements in the specified collection equal to the specified object. |
| indexOfSubList(List<?> source, List<?> target) | This method returns the starting position of the first occurrence of the specified target list within the specified source list, or -1 if there is no such occurrence. |
| lastIndexOfSubList(List<?> source, List<?> target) | This method returns the starting position of the last occurrence of the specified target list within the specified source list, or -1 if there is no such occurrence. |
| list(Enumeration<T> e) | This method returns an array list containing the elements returned by the specified enumeration in the order they are returned by the enumeration. |
| max(Collection<? extends T> coll) | This method returns the maximum element of the given collection, according to the natural ordering of its elements. |
| max(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp) | This method returns the maximum element of the given collection, according to the order induced by the specified comparator. |
| min(Collection<? extends T> coll) | This method returns the minimum element of the given collection, according to the natural ordering of its elements. |
| min(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp) | This method returns the minimum element of the given collection, according to the order induced by the specified comparator. |
| nCopies(int n, T o) | This method returns an immutable list consisting of n copies of the specified object. |
| newSetFromMap(Map<E,Boolean> map) | This method returns a set backed by the specified map. |
| replaceAll(List<T> list, T oldVal, T newVal) | This method replaces all occurrences of one specified value in a list with another. |
| reverse(List<?> list) | This method reverses the order of the elements in the specified list |
| reverseOrder() | This method returns a comparator that imposes the reverse of the natural ordering on a collection of objects that implement the Comparable interface. |
| reverseOrder(Comparator<T> cmp) | This method returns a comparator that imposes the reverse ordering of the specified comparator. |
| rotate(List<?> list, int distance) | This method rotates the elements in the specified list by the specified distance. |
| shuffle(List<?> list) | This method randomly permutes the specified list using a default source of randomness. |
| shuffle(List<?> list, Random rnd) | This method randomly permute the specified list using the specified source of randomness. |
| singletonMap(K key, V value) | This method returns an immutable map, mapping only the specified key to the specified value. |
| singleton(T o) | This method returns an immutable set containing only the specified object. |
| singletonList(T o) | This method returns an immutable list containing only the specified object. |
| sort(List<T> list) | This method sorts the specified list into ascending order, according to the natural ordering of its elements. |
| sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) | This method sorts the specified list according to the order induced by the specified comparator. |
| swap(List<?> list, int i, int j) | This method swaps the elements at the specified positions in the specified list. |
| synchronizedCollection(Collection<T> c) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) collection backed by the specified collection. |
| synchronizedList(List<T> list) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) list backed by the specified list. |
| synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) map backed by the specified map. |
| synchronizedNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K,V> m) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) navigable map backed by the specified navigable map. |
| synchronizedNavigableSet(NavigableSet<T> s) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) navigable set backed by the specified navigable set. |
| synchronizedSet(Set<T> s) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) set backed by the specified set. |
| synchronizedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) sorted map backed by the specified sorted map. |
| synchronizedSortedSet(SortedSet<T> s) | This method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) sorted set backed by the specified sorted set. |
| unmodifiableCollection(Collection<? extends T> c) | This method returns an unmodifiable view of the specified collection. |
| unmodifiableList(List<? extends T> list) | This method returns an unmodifiable view of the specified list. |
| unmodifiableNavigableMap(NavigableMap<K,? extends V> m) | This method returns an unmodifiable view of the specified navigable map. |
| unmodifiableNavigableSet(NavigableSet<T> s) | This method returns an unmodifiable view of the specified navigable set. |
| unmodifiableSet(Set<? extends T> s) | This method returns an unmodifiable view of the specified set. |
| unmodifiableSortedMap(SortedMap<K,? extends V> m) | This method returns an unmodifiable view of the specified sorted map. |
| unmodifiableSortedSet(SortedSet<T> s) | This method returns an unmodifiable view of the specified sorted set. |